COVID-19 pandemic may be "GOOD" news for India’s economy or may be "BAD" for China
 |
| Click to enlarge view |
Due to the adoption of free-market principles in China, it has become emerging market economy and one of the world’s most hyped investment locations due to promising opportunity to many companies and investors.
An overview on China Economy:
“In 2019, Chinese companies signed 6,944 newly foreign contracted projects in 62 countries including ‘Belt and Road Routes’ at a value of $154.89 Billion.”
China is the second largest economy in the world with GDP of $14.4 Trillion (2019). But, in 1950s, it was counted among the poor society and from 1978, under the leadership of Chinese leader Deng Xiaoping (China’s Economic Reformer) and Chinese government decided to break with its Soviet style economic policies by gradually reforming the economy according to free-market principles. And opening up trade and investment with the West, in the hope that this would significantly increase economic growth and raise living standards keep focus on Heavy Industries for the economy growth. And today, China is the world leader in manufacturing and also produces almost half of the world’s crude steel (World 1,869.9 Mt and China 996.3 Mt in 2019).
Due to the Covid-19 outbreak in China, in the first quarter (Q1) of 2020, Foreign direct investment (FDI) fell to 10.8 percent Year-over-Year (YOY) to $31.2 Billion (216.19 Billion Yuan), where as in previous year 2019 of first quarter, FDI in China grew 5.8 per cent from a YOY to $ 136.71Billion (941.5 Billion Yuan). Though Outbound Investment Declined (OID) to 8.2 percent YOY to $110.6 Billion and amid continuing capital controls.
 |
| Click to enlarge view |
These sharp increases in China’s global FDI outflows in recent years appears to be largely driven by a number of factors, including government policies and initiatives of that country to encourage firms to “Go-Global.” The Chinese government wants to use FDI to gain access to Intellectual Property Rights (IPR), Technology, famous brands, etc., in order to move Chinese firms up the value-added chain in manufacturing and services, boost domestic innovation and development of Chinese brands, and help Chinese State-Owned Enterprise (SOEs) to become major global competitors.
After the COVID19 pandemic, Chinese Government is encouraging to re-open Factories, Business, Shops, Dinning and transport but it seems that still china economy slowdown. The problem facing China now is that it’s mostly back in business, but the global shutdown has caused clients and orders to disappear.
An overview of China’s Import and Export:
“China has 24 Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) under construction, among which 16 Agreements have been signed and already implemented.”
China’s factories are resuming production, but pandemic-triggered recessions around the world have manufacturers pessimistic about export demand. China’s official index of manufacturing purchasing managers slipped to 50.8 in April. That is down from 52.0 in March, when it bounced back strongly from February’s dismal 35.7.
 |
| Click to enlarge view |
But, on the other hand, the exports of China in past 2 months of year 2020 has been recorded in month of February was $292.45 Billion and March was $185.15 Billion, whereas the import has been recorded month of February $299.54 Billion and March was $165.25 Billion. Info-graphic shows the China’s import and export from Jan-2017 to March-2020.
 |
| Click to enlarge view |
Currently, China has 24 Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) under construction, among which 16 Agreements have been signed and already implemented. FTA is an effective approach to integrate into global economy and strengthen economic cooperation with other economies, as well as particularly an important supplement to Multilateral Trading Agreements between among three or more nations.
Current Indian Economy:
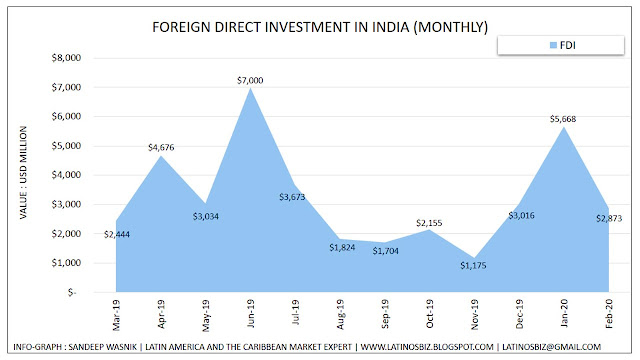
“Foreign Direct Investment in India averaged $1412.87 Million from 1995 until 2020. Although, During COVID-19 pandemic, FDI in India increased by $2873Million in February of 2020 and could be expected to 4000 Million by the end of this quarter.”
The economy will suffer in FY 2020, which started in April, due to containment measures and weaker external demand and growth projection for India to 1.9% from 5.8% projected in January, holding that the ‘Extension of Lockdown’ to combat the covid-19 outbreak will throw the world economy into the worst recession since the great Depression in 1930s. More positively, however, fiscal stimulus should cushion the economic blow, as should the supply of funds be expanded and easily accessible to Industries and entrepreneur to encourage economic growth (Loose Monetary Policy).
India’s Manufacturing PMI fell to 27.4 in April 2020 from 51.8 in the previous month and far below market consensus of 42 and India’s Services PMI fall to 5.4 in April 2020 from 49.3, and far below market expectations of 40.0. The latest reading pointed to the second straight month of contraction in the sector, due to the impact COVID19 pandemic, amid restrictions on the movement of citizens and business shutdowns. But, In the second quarter, Indian economy could pick up as industries restart their operations with the streamlining of supply chains.
 |
| Click to enlarge view |
There are 231 operational Special Economic Zone (SEZ) and around 355 SEZ that are notified in India. COVID-19 pandemic may be good news for Indian competitiveness and capital inflows as long as the government can match after the second quarter of 2020 recovery by providing incentives and other advantages for foreign investors that complement their business plans in India. Ultimately, however, the benefits of India’s SEZ policy have been substantial as it is one of the reasons why there is an increase in the number of foreign firms operating in India.
Foreign Direct Investment in India averaged $1412.87 Million from 1995 until 2020. Although, During COVID-19 pandemic, FDI in India increased by $2873Million in February of 2020 and could be expected to 4000 Million by the end of this quarter.
 |
| Click to enlarge view |
An overview of Indian Industries:
"Nearly 75 Million enterprises are in India and about 45% contribute to manufacturing output."
The Indian Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) sector is the backbone of the national economic structure. In India approximately 97 percent of the industries fall under the category of MSMEs and the strongest drivers of economic development, innovation, employment, and also contributes 31% of India’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP). Nearly 75 Million enterprises are in India and about 45% contribute to manufacturing output, more than 45% contribute to Indian exports and creating about 114 million employments. Some Indian enterprises are engaged directly in exports and most of the MSMEs are indirectly engaged in the export’s ecosystem through intermediate goods manufacturing for larger industries as well as engaged in exports to international partners.
Due to the COVID19 lockdown from March 24, 2020 in India, this has badly impacted MSMEs and the contribution of 31% of Indian GDP already gone down. Nearly 25 per cent of firms are on the way to permanently shut down, and more than 60% firm not have funds to pay salary.
“Make in India” initiative has the potential to turn the Indian economy upside, all for better reasons. With the investment in the manufacturing sector and the advancement of technology, employment opportunities can also be generated. Such an initiative requires a well-coordinated effort from the Ministry of Commerce and Industry as well as the state governments.
India’s Import and Export:
"India has 42 Trade Agreements (Including PTAs), where 13 are in effect, 16 are under negotiation, 12 are proposed/under negotiation/study and 1 is signed but not yet implemented."
Currently, there are 70 million traders and the majority of them are MSME in India. These MSMEs are also depended on Chinese raw, semi-finished and Finished products, Like, Electronic Goods, Cellphones and its parts, Electric Machineries, Pharmaceutical API, Iron and Steel, Raw Material, Auto Parts and others. Due to the COVID19, the exports from China to India has been suddenly dropped, this hit to Indian MSMEs. India needs focus on Products manufacturing under the Make in India Programme and slowly eliminate the dependency on China Imports.
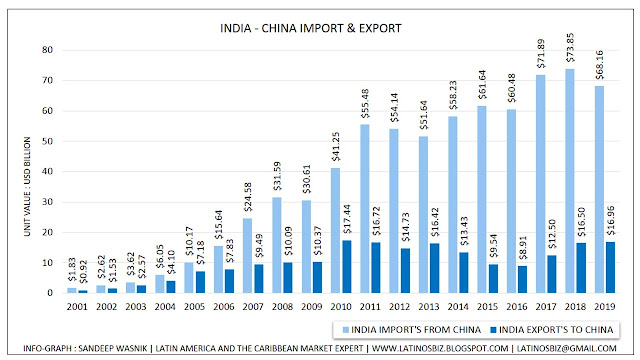
For India, China is the biggest trading partner, India imports $480 Billion valued product from around the world, in which $68.16 Billion valued of products from China, where India exports $322.786 Billion valued product to the world and exports to China $16.96 Billion valued products in 2019.
 |
| Click to enlarge view |
In Asia, India is one among top countries withholding maximum number of Free Trade Agreement (FTAs) and Preferential Trade Agreements (PTAs) either in operation or under negotiation or proposed and most of them existing with Asian countries which are quite different from each other in terms of the level of their economic development.
According to the Asian Development Bank Institute, India has 42 Trade Agreements (Including PTAs), where 13 are in effect, 16 are under negotiation, 12 are proposed/under negotiation/study and 1 is signed but not yet implemented.
India still needs to focus on more trade agreements to boost the bilateral trade, Although, Trade agreements are an effective approach to integrate into global economy and strengthen economic cooperation with other economies.
👉 Click here to read on The Financial Express
Article by Sandeep Wasnik | Latin America & the Caribbean Countries Affairs and Market Expert
Contact : latinosbiz@gmail.com






